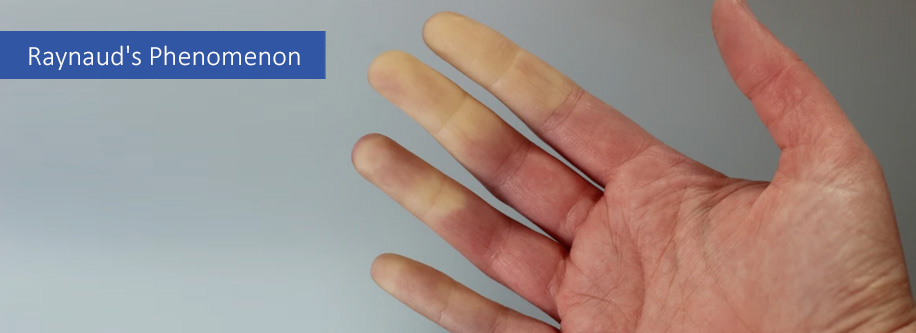
When the pathology is accompanied by another disease
- Autoimmune diseases (scleroderma, systemic lupus erythematosus)
- Hematological diseases (cryoglobulinemia, paraneoplastic syndrome)
- Hypothyroidism
- Atherosclerosis, vasculitis, obliterating thromboangiitis, thoracic outlet syndrome
- Carpal tunnel syndrome
- Medicines (cocaine, nicotine, interferon, some drugs used during chemotherapy)
- Autoimmune hepatitis
- Diabetes mellitus
Secondary Raynaud’s phenomenon is characterized by a more severe course, and as a complication, ulcers and necrosis may develop on the fingers.
Confirming the diagnosis and identifying the type of Raynaud’s phenomenon is important in planning treatment. Primary Raynaud’s phenomenon often does not require the inclusion of drugs in the treatment, and mainly the correct definition of lifestyle is important (avoid being in the cold, wear warm gloves and socks, stop smoking), in case the symptoms worsen the quality of life, the issue of drug treatment is considered. In the case of secondary Raynaud’s, the treatment is more difficult and complex, the most important thing is to treat the underlying disease.