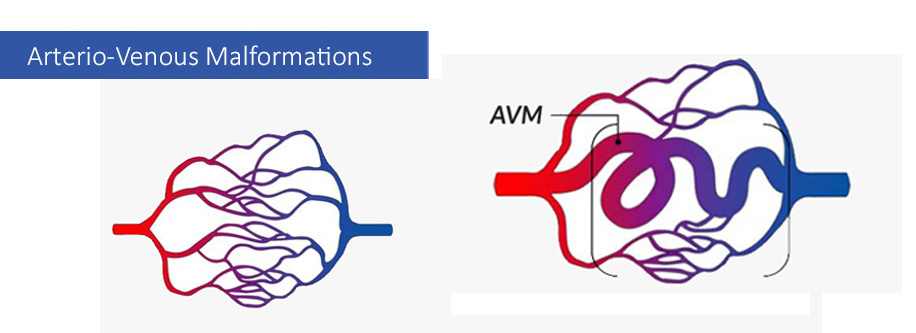
Arteriovenous malformation is a pathological connection of arteries and veins, due to which normal blood movement and oxygen circulation are disturbed. Arteries are responsible for delivering oxygen-rich blood to the tissues, while veins carry oxygen-poor blood away from the tissues. During arterio-venous malformation, this cycle is disturbed, due to which the walls of blood vessels can be thinned and burst.
Arteriovenous Malformations
Arteriovenous Malformations
The Underlying Causes
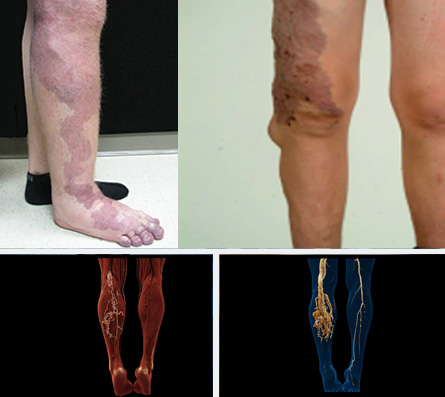
Basically, arteriovenous malformation causes an increase in the size of the tissue, as the arteries and veins expand, the surrounding tissue also grows larger than the healthy tissue. In many cases, the disease begins asymptomatically, we can only notice slight redness and heat of the skin. As the disease progresses, blood vessels become visible. In more severe cases, it can cause damage to the surrounding tissues, pain, sores or ulcers, and possible bleeding. It is difficult to predict disease progression and complications.
Methods of Treatment
Angiography
Angiography helps to visualize the network of blood vessels. After diagnosis, the main method of treatment is endovascular (embolization) and sclerotherapy.
Embolisation
Embolization is a minimally invasive non-surgical procedure in which a blood vessel is selectively occluded with special emboli. The procedure is carried out with X-ray control. Embolization is an alternative to surgical intervention and is aimed at severing the pathological arterio-venous connection.
Artificial Embolus
Artificial emboli of different shapes are used for blood vessel embolization: spirals, particles, and cylinders. In addition, they secrete liquid embolizing, desclerosing agents.
Liquid Embolic Substances
Liquid embolizing substances – used mainly for the treatment of arteriovenous malformation, freely penetrate into the complex vascular network, which is why there is no need to insert a catheter into a separate blood vessel.
Also Used
Embolizing microparticles – Embolizing microparticles are used in small arteries and precapillary arterioles, mainly useful for deep-seated arteriovenous malformations.
Mechanical embolization – for the purpose of mechanical occlusion, embolizing spirals and removable balloons are used, which are useful in case of any blood vessel. Its advantage lies in the fact that they can be placed exactly where occlusion is required.
During sclerotherapy, sclerosing substances are injected into the pathological A-V network by micropuncture, which causes hardening of the lining endothelium of the blood vessel. They have a slow embolizing effect compared to liquid means, so they cannot be used for embolization of large vessels with a strong blood supply.